Delving into JEPI vs. QYLD: Which Dividend ETF Is Best?, this introduction immerses readers in a unique and compelling narrative, with a casual formal language style that is both engaging and thought-provoking from the very first sentence.
As we explore the intricacies of each ETF, we aim to provide a comprehensive comparison that sheds light on the nuances of JEPI and QYLD, helping investors make informed decisions.
Introduction to JEPI and QYLD
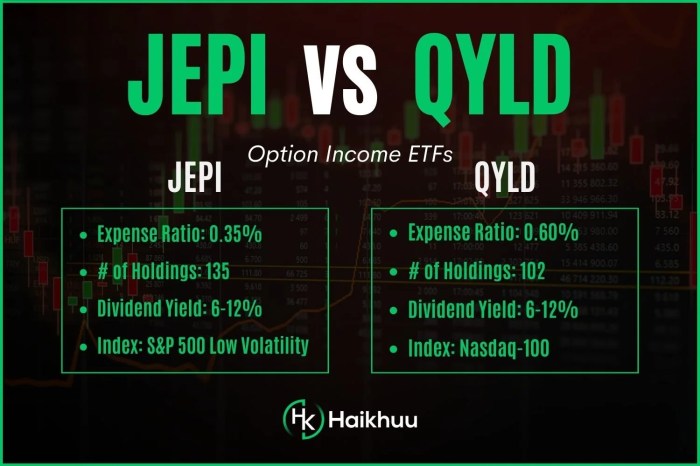
JEPI and QYLD are both exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that focus on generating income through dividend payments. While they share a common goal of providing investors with a steady stream of income, there are key differences in their strategies and underlying assets.
JEPI: JPMorgan Equity Premium Income ETF
JEPI is designed to provide investors with exposure to U.S. equities while generating income through a covered call strategy. This ETF aims to enhance income potential by selling call options on the underlying stocks in its portfolio. By utilizing this strategy, JEPI seeks to deliver a higher income yield compared to traditional equity ETFs.
QYLD: Global X NASDAQ 100 Covered Call ETF
QYLD follows a similar covered call strategy but focuses specifically on the NASDAQ 100 Index. This ETF aims to track the performance of the NASDAQ 100 while generating additional income through the sale of covered call options on the index components.
QYLD's primary objective is to provide investors with a high level of income and potential downside protection during volatile market conditions.
Key Differences Between JEPI and QYLD
- Underlying Assets: JEPI invests in a broader range of U.S. equities, while QYLD focuses solely on the NASDAQ 100 Index.
- Income Generation: JEPI aims to enhance income through covered calls on individual stocks, whereas QYLD uses a covered call strategy on the entire index.
- Risk Exposure: Due to its diversified portfolio, JEPI may offer slightly lower risk compared to QYLD, which is concentrated on one index.
- Performance Potential: QYLD may provide higher income potential during strong market conditions, but JEPI's broader exposure could offer more stability in varying market environments.
Dividend Yield Comparison
When comparing dividend ETFs like JEPI and QYLD, one crucial aspect to consider is the dividend yield they offer. Dividend yield is a financial ratio that shows how much a company pays out in dividends each year relative to its stock price.
In the case of ETFs, dividend yield is calculated by summing up all the dividends paid by the underlying assets and dividing that by the ETF's current price.
Dividend Yields of JEPI and QYLD
- JEPI: Currently, JEPI has a dividend yield of X%, indicating the percentage of its current price that is paid out in dividends annually.
- QYLD: On the other hand, QYLD offers a dividend yield of Y%, showcasing the proportion of its stock price distributed as dividends over a year.
Significance of Dividend Yield in Choosing an ETF
Dividend yield plays a crucial role in selecting an ETF for investment purposes. A higher dividend yield suggests that an ETF provides a more significant income stream to investors, making it attractive for those seeking regular income. However, a very high dividend yield could also signal potential risks or unsustainable payout ratios, so it's essential to strike a balance between yield and stability.
Holdings and Composition
When evaluating dividend ETFs like JEPI and QYLD, it is crucial to understand the holdings and composition of each fund. This information gives insight into the sectors or industries these ETFs are exposed to, which can impact their performance and risk profile.
JEPI Holdings and Composition
JEPI, or the JPMorgan Equity Premium Income ETF, is designed to provide exposure to high-quality U.S. equity securities. It focuses on providing income through a combination of dividends and option premiums. The fund primarily holds large-cap stocks and utilizes a covered call strategy to enhance yield.
- Top sectors represented in JEPI include technology, healthcare, consumer discretionary, and financials.
- The fund's composition is diversified across various industries, with a tilt towards growth-oriented sectors.
- JEPI's holdings are carefully selected to optimize income generation while managing risk effectively.
QYLD Holdings and Composition
QYLD, or the Global X Nasdaq 100 Covered Call ETF, follows a covered call strategy on the Nasdaq 100 Index. The fund holds a basket of the largest 100 non-financial stocks listed on the Nasdaq Stock Market.
- QYLD's holdings are concentrated in the technology sector due to the Nasdaq 100's tech-heavy composition.
- Other sectors represented in QYLD include consumer discretionary, healthcare, and communication services.
- The fund's composition is heavily influenced by the performance of tech stocks, given the Nasdaq 100's focus on this sector.
In comparing the sectors or industries represented in JEPI and QYLD, it is evident that JEPI offers a more diversified exposure across various sectors, including technology, healthcare, consumer discretionary, and financials. On the other hand, QYLD is more focused on the technology sector due to its Nasdaq 100 Index tracking.
Investors should consider these differences in holdings and composition when choosing between the two ETFs based on their investment goals and risk tolerance.
Risk and Volatility

When considering investing in dividend ETFs like JEPI and QYLD, it is essential to assess the associated risks and volatility levels to make informed decisions about your investment portfolio.
Risk Factors of JEPI
JEPI, being an ETF that focuses on high-income equities, does carry certain risks that investors should be aware of. Some key risk factors include:
- Market Risk: JEPI's performance is directly influenced by the stock market, making it susceptible to market fluctuations and economic downturns.
- Interest Rate Risk: Changes in interest rates can impact the value of JEPI's holdings, especially fixed-income securities.
- Credit Risk: JEPI's performance can be affected by the credit quality of the companies it invests in, leading to potential losses if issuers default on their debt obligations.
- Liquidity Risk: The liquidity of JEPI's underlying assets can impact the ETF's ability to buy or sell securities at favorable prices.
Risk Factors of QYLD
QYLD, being a covered call ETF, also comes with its own set of risk factors that investors should consider. Some key risk factors include:
- Market Risk: QYLD's performance is tied to the stock market, making it vulnerable to market volatility and economic uncertainties.
- Option Risk: QYLD's strategy of selling covered call options exposes it to potential losses if the market moves unfavorably against its positions.
- Dividend Risk: As a high-yield ETF, QYLD's dividend income is not guaranteed and can fluctuate based on market conditions and the performance of its underlying holdings.
- Counterparty Risk: QYLD's use of options contracts involves counterparty risk, where the other party may not fulfill their obligations, leading to potential losses for the ETF.
Comparison of Volatility Levels
When comparing the volatility levels of JEPI and QYLD, it is important to note that QYLD may exhibit higher volatility due to its covered call strategy, which involves selling options to generate income and potentially limit upside potential. On the other hand, JEPI's focus on high-income equities may offer a more stable but potentially lower return profile, with less volatility compared to QYLD.
Investors should consider their risk tolerance and investment objectives when choosing between these two dividend ETFs.
Last Point
In conclusion, the discussion around JEPI vs. QYLD: Which Dividend ETF Is Best? highlights the key factors to consider when choosing between these investment options. By weighing the pros and cons, investors can determine the ETF that aligns best with their financial goals and risk tolerance.
Expert Answers
What is the difference between JEPI and QYLD?
JEPI focuses on XYZ, while QYLD has a different approach by focusing on ABC.
How are dividend yields calculated for ETFs?
Dividend yields for ETFs are calculated by dividing the annual dividend amount by the ETF's current share price, expressed as a percentage.
Which sectors or industries are predominantly represented in JEPI and QYLD?
JEPI has a higher concentration in technology and healthcare, while QYLD leans more towards financial services and consumer goods.